Conclusion 以下的內容其實不少,先把重點抓到這裡來:
Term Query & Full Text Query 重點整理
Term Query 不會做分詞處理,而 Full Text Query 會做分詞處理
要做精準搜尋,使用 [FIELD_NAME].keyword 欄位
透過 Constant Score query(將關鍵字 term 改成 constant_score + filter + term),可以將查詢轉換為 filter,跳過算分(scoring)步驟並可利用 cache 來加速查詢效能
若是要快速將不需要的資料過濾掉,constant score query 是很好的一個方式
Term 是表達語意的最小單位,搜尋或是利用自然語言進行處理時都需要處理 term
查詢的語法中,只要指定 term(query >> term ) 關鍵字,就表示使用 term query
Term Level Query 包含 Term Query / Range Query / Exists Query / Prefix Query / Wildcard Query
當 ES 接收到 term query 時,對輸入不會進行分詞,而是將輸入當作一個整體在 inverted index 中找到精確的詞項,並使用相關度算分的機制來計算分數
若是不需要算分,則可以利用 constant score 將查詢轉換成 filter,並利用 cache 來提高效能
以下使用範例說明 term 查詢所需要注意的事項:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 PUT products { "settings" : { "number_of_shards" : 1 } } POST /products/_bulk { "index" : { "_id" : 1 } } { "productID" : "XHDK-A-1293-#fJ3" , "desc" : "iPhone" } { "index" : { "_id" : 2 } } { "productID" : "KDKE-B-9947-#kL5" , "desc" : "iPad" } { "index" : { "_id" : 3 } } { "productID" : "JODL-X-1937-#pV7" , "desc" : "MBP" } GET /products POST /products/_search { "query" : { "term" : { "desc" : { "value" : "iPhone" } } } } POST /products/_search { "query" : { "term" : { "desc.keyword" : { "value" : "iPhone" } } } } POST /products/_search { "query" : { "term" : { "productID" : { "value" : "XHDK-A-1293-#fJ3" } } } } POST /products/_search { "query" : { "term" : { "productID.keyword" : { "value" : "XHDK-A-1293-#fJ3" } } } } POST /products/_search { "query" : { "constant_score" : { "filter" : { "term" : { "productID.keyword" : "XHDK-A-1293-#fJ3" } } } } }
Full text query 可以是 match query, match phrase query, query string query … 等等,詳細的列表可以參考官網資料
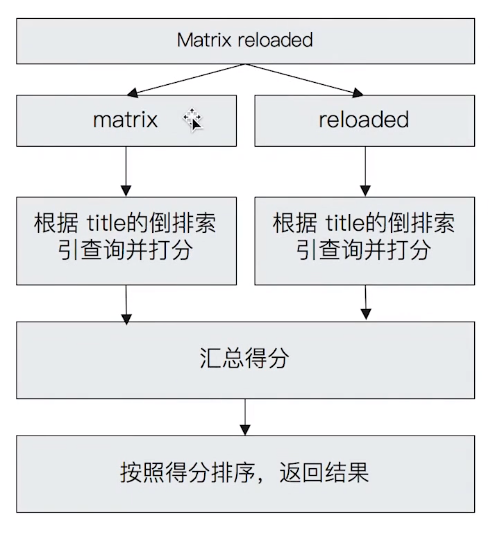
index & query 都會進行分詞,查詢字串會先傳給一個合適的 analyzer,並生成用來查詢的 term list
分詞後的 term list 會被逐一拿來查詢,並將最後結果合併後,為每個 document 計算出一個分數
以下是幾個簡單範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 POST /movies/_search { "query" : { "match" : { "title" : { "query" : "Matrix reloaded" } } } } POST /movies/_search { "query" : { "match_phrase" : { "title" : { "query" : "Matrix reloaded" } } } }
Match Query 的查詢過程
屬於 Full Text Qeury:包含了 Match Query、Match Phrase Query、Query String Query
Document 被索引 & 搜尋時都會經過分詞處理,然後產生提供查詢的詞項列表
查詢時會根據詞項列表逐一查詢,再將結果合併後,為每一個 document 進行算分(scoring)
結構化搜尋 結構化數據
像是 date, boolean, number … 這一類的數據都是屬於結構化的
有些 text 也屬於結構化的,例如:顏色(red, green, blue)、tag(distributed, search)、特定編碼….只要有遵守規定產生的 text,都可以算是結構化的格式
而結構化搜尋就是對結構化的數據進行搜尋
以下是一些簡單範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 DELETE products POST /products/_bulk { "index" : { "_id" : 1 } } { "price" : 10 , "avaliable" : true , "date" : "2018-01-01" , "productID" : "XHDK-A-1293-#fJ3" } { "index" : { "_id" : 2 } } { "price" : 20 , "avaliable" : true , "date" : "2019-01-01" , "productID" : "KDKE-B-9947-#kL5" } { "index" : { "_id" : 3 } } { "price" : 30 , "avaliable" : true , "productID" : "JODL-X-1937-#pV7" } { "index" : { "_id" : 4 } } { "price" : 30 , "avaliable" : false , "productID" : "QQPX-R-3956-#aD8" } GET products/_mapping POST products/_search { "profile" : "true" , "explain" : true , "query" : { "term" : { "avaliable" : true } } } POST products/_search { "profile" : "true" , "explain" : true , "query" : { "constant_score" : { "filter" : { "term" : { "avaliable" : true } } } } } GET products/_search { "query" : { "constant_score" : { "filter" : { "range" : { "price" : { "gte" : 20 , "lte" : 30 } } } } } } POST products/_search { "query" : { "constant_score" : { "filter" : { "range" : { "date" : { "gte" : "now-2y" } } } } } } GET /movies/_search { "query" : { "prefix" : { "year" : "201" } } } POST /movies/_bulk { "index" : { "_id" : 1 } } { "title" : "Father of the Bridge Part II" , "year" : 1995 , "genre" : "Comedy" } { "index" : { "_id" : 2 } } { "title" : "Dave" , "year" : 1993 , "genre" : [ "Comedy" , "Romance" ] } POST /movies/_search { "query" : { "constant_score" : { "filter" : { "term" : { "genre.keyword" : "Comedy" } } } } }
搜索的相關性算分 相關性 & 相關性算分
Term Frequency (詞頻) & 逆文檔頻率(Inverse Document Frequency, IDF)
檢索詞在一篇 document 中出現的頻率 = 檢索詞出現的次數 / document 總字數
衡量查詢 & 結果 document 相關性的簡單方法就是將每個 term 的 TF 相加 = TF(word1) + TF(word2) + TF(word3)
stop word 出現太多,一般計算分數時不會列入考慮
IDF = log(全部 document 數量 / 檢索詞出現過的 document 總數)
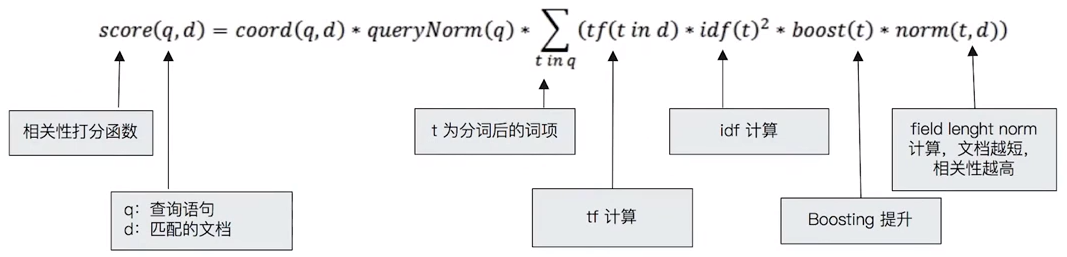
TF-IDF 其實就是從 sum(TF) 變成了 sum(TF + IDF)
現代的 search engine 大多以 TF-IDF 為基礎再加上大量的優化
從上圖可見,TF-IDF 的評分公式,除了 TD & IDF 之外,還包涵了 boosting & field length(欄位長度) 兩項
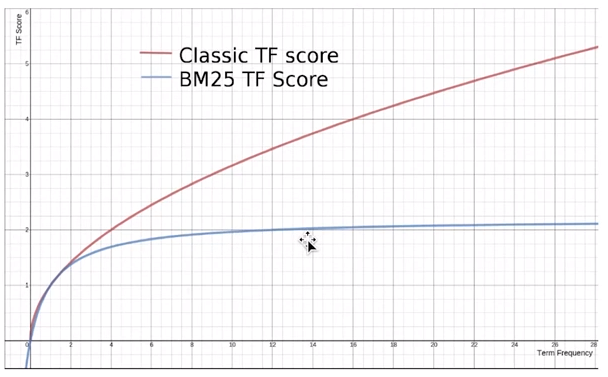
BM 25
跟 TF-IDF 相比,當 TF 無限增加時,BM 25 算分會趨近於某個值,不會無限變大
Boosting Relevance
boosting 是可以用來控制相關度的一種方式,可用在 index, field, 或是查詢子條件中
當 boost > 1 可提昇相關度,0 < boost < 1 計算分數的權重相對降低, boost < 0,貢獻為負分
以下是一個簡單的範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 PUT /testscore/_bulk { "index" : { "_id" : 1 } } { "content" : "we use Elasticsearch to power the search" } { "index" : { "_id" : 2 } } { "content" : "we like elasticsearch" } { "index" : { "_id" : 3 } } { "content" : "The scoring of documents is caculated by the scoring formula" } { "index" : { "_id" : 4 } } { "content" : "you know, for search" } POST /testscore/_search { "explain" : true , "query" : { "match" : { "content" : "elasticsearch" } } } POST testscore/_search { "explain" : true , "query" : { "boosting" : { "positive" : { "term" : { "content" : "elasticsearch" } } , "negative" : { "term" : { "content" : "like" } } , "negative_boost" : 0.2 } } }
Query & Filtering 與多字符串多字段查詢 Query Context & Filter Context
Bool Query
一個 bool query 是一個 or 多個查詢子句所組成 (可組合成複合查詢)
子句
效果
must(Query Context ) 必須符合,對算分有貢獻
should(Query Context ) 選擇性符合,對算分有貢獻
must_not(Filter Context ) 必須不能符合,對算分無貢獻
filter(Filter Context ) 必須符合,對算分無貢獻
bool query 中的每一個查詢子句得到的分數都會被合併成總和的相關性評分
關於查詢的語法,有以下幾點需要注意:
範例 包含多個子查詢的 Bool Query 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 POST /products/_bulk { "index" : { "_id" : 1 } } { "price" : 10 , "avaliable" : true , "date" : "2018-01-01" , "productID" : "XHDK-A-1293-#fJ3" } { "index" : { "_id" : 2 } } { "price" : 20 , "avaliable" : true , "date" : "2019-01-01" , "productID" : "KDKE-B-9947-#kL5" } { "index" : { "_id" : 3 } } { "price" : 30 , "avaliable" : true , "productID" : "JODL-X-1937-#pV7" } { "index" : { "_id" : 4 } } { "price" : 30 , "avaliable" : false , "productID" : "QQPX-R-3956-#aD8" } POST /products/_search { "query" : { "bool" : { "must" : { "term" : { "price" : "30" } } , "filter" : { "term" : { "avaliable" : "true" } } , "must_not" : { "range" : { "price" : { "lte" : 10 } } } , "should" : [ { "term" : { "productID.keyword" : "JODL-X-1937-#pV7" } } , { "term" : { "productID.keyword" : "XHDK-A-1293-#fJ3" } } ] , "minimum_should_match" : 1 } } }
複雜的 Bool Query 在 bool query 中再放入一個 bool query:(多層 bool query 的概念)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 POST /products/_search { "query" : { "bool" : { "must" : { "term" : { "price" : "30" } } , "should" : [ { "bool" : { "must_not" : { "term" : { "avaliable" : "false" } } } } ] , "minimum_should_match" : 1 } } }
不同的算分標準 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 POST /animals/_search { "query" : { "bool" : { "should" : [ { "term" : { "text" : "brown" } } , { "term" : { "text" : "red" } } , { "term" : { "text" : "quick" } } , { "term" : { "text" : "dog" } } ] } } } POST /animals/_search { "query" : { "bool" : { "should" : [ { "term" : { "text" : "quick" } } , { "term" : { "text" : "dog" } } , { "bool" : { "should" : [ { "term" : { "text" : "brown" } } , { "term" : { "text" : "brown" } } , ] } } ] } } }
搭配 boosting 進行查詢 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 DELETE news POST /news/_bulk { "index" : { "_id" : 1 } } { "content" : "Apple Mac" } { "index" : { "_id" : 2 } } { "content" : "Apple iPad" } { "index" : { "_id" : 3 } } { "content" : "Apple employee like Apple Pie and Apple Juice" } POST /news/_search { "query" : { "bool" : { "must" : { "match" : { "content" : "apple" } } } } } POST /news/_search { "query" : { "bool" : { "must" : { "match" : { "content" : "apple" } } , "must_not" : { "match" : { "content" : "pie" } } } } } POST /news/_search { "query" : { "boosting" : { "positive" : { "match" : { "content" : "apple" } } , "negative" : { "match" : { "content" : "pie" } } , "negative_boost" : 0.5 } } }
單字符串多字段查詢:Disjunction Max Query 一般在進行 single string multiple field 的查詢時,預設的分數計算方式過於簡單,往往會出現非使用者所預期的情況,例如以下範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 DELETE blogs POST /blogs/_bulk { "index" : { "_id" : 1 } } { "title" : "Quick brown rabbits" , "body" : "Brown rabbits are commonly seen." } { "index" : { "_id" : 2 } } { "title" : "Keeping pets healthy" , "body" : "My quick brown fox eats rabbits on a regular basis." } POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "bool" : { "should" : [ { "match" : { "title" : "Brown fox" } } , { "match" : { "body" : "Brown fox" } } ] } } } POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "dis_max" : { "queries" : [ { "match" : { "title" : "Brown fox" } } , { "match" : { "body" : "Brown fox" } } ] } } }
因此從上面的範例來看,透過 Disjunction Max Query 可以找到最符合查詢條件的結果。
但 Disjunction Max Query 也並非萬靈丹,因為其算分方式也是有盲點的,例如以下範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "dis_max" : { "queries" : [ { "match" : { "title" : "Quick pets" } } , { "match" : { "body" : "Quick pets" } } ] } } } POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "dis_max" : { "queries" : [ { "match" : { "title" : "Quick pets" } } , { "match" : { "body" : "Quick pets" } } ] , "tie_breaker" : 0.2 } } }
關於 Disjunction Max Query & tie_breaker 的搭配,可以參考官方文件 說明。
單字符串多字段查詢:Multi Match 一般 single string multiple field 的查詢,會發生在三個場景:
每個 field 之間會互相競爭,搜尋時會把評分最高的 field 中的資料回傳(可以額外加上 tie_breaker or minumum_should_match 來調整搜尋精準度)
通常會使用在英文的內容時,通常會在 main field 中設定 English Analyzer,並加入同義詞來試圖符合更多的 document,並適時的 text 中加入 sub field 搭配 standard Analyzer 盡量保留原始訊息,以提供更精確的搜尋結果
某些訊息需要同時在多個 field 查詢時,可以做一種類似多(single string -> multi words)對多(multi field)的搜尋
首先使用以下幾個範例來說明 Best Field :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 DELETE blogs POST /blogs/_bulk { "index" : { "_id" : 1 } } { "title" : "Quick brown rabbits" , "body" : "Brown rabbits are commonly seen." } { "index" : { "_id" : 2 } } { "title" : "Keeping pets healthy" , "body" : "My quick brown fox eats rabbits on a regular basis." } POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "dis_max" : { "queries" : [ { "match" : { "title" : "Quick pets" } } , { "match" : { "body" : "Quick pets" } } ] } } } POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "multi_match" : { "type" : "best_fields" , "query" : "Quick pets" , "fields" : [ "title" , "body" ] } } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 DELETE titles PUT /titles { "mappings" : { "properties" : { "title" : { "type" : "text" , "analyzer" : "english" } } } } POST titles/_bulk { "index" : { "_id" : 1 } } { "title" : "My dog barks" } { "index" : { "_id" : 2 } } { "title" : "I see a lot of barking dogs on the road " } GET titles/_search { "query" : { "match" : { "title" : "barking dogs" } } }
從上面可以看出 best field 在某些時候的確會有一些盲點,因此我們可以試著使用以下方法來調整:
也可以根據需求適時加入 boosting 設定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 DELETE /titles PUT /titles { "mappings" : { "properties" : { "title" : { "type" : "text" , "analyzer" : "english" , "fields" : { "std" : { "type" : "text" , "analyzer" : "standard" } } } } } } POST titles/_bulk { "index" : { "_id" : 1 } } { "title" : "My dog barks" } { "index" : { "_id" : 2 } } { "title" : "I see a lot of barking dogs on the road " } GET /titles/_search { "query" : { "multi_match" : { "query" : "barking dogs" , "type" : "most_fields" , "fields" : [ "title" , "title.std" ] } } } GET /titles/_search { "query" : { "multi_match" : { "query" : "barking dogs" , "type" : "most_fields" , "fields" : [ "title^10" , "title.std" ] } } }
接著如果我們需要針對更複雜的資料(例如:地址),並同時在多個 field 中做搜尋,則可以藉由 cross_fields 來取得更精確的搜尋結果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 PUT address/_doc/1 { "street" : "5 Poland Street" , "city" : "London" , "country" : "United Kingdom" , "postcode" : "W1V 3DG" } POST address/_search { "query" : { "multi_match" : { "query" : "Poland Kingdom W1V" , "type" : "cross_fields" , "operator" : "and" , "fields" : [ "street" , "city" , "country" , "postcode" ] } } }
若使用 copy_to 的方式解決,就需要額外的儲存空間
全文檢索案例 思考 & 分析
Full text query or Term query
針對搜尋的條件 & field,定義合適的 analyzer 是很重要的
開發時需要對不同的 analyzer 做測試
透過調整 mapping 設定,並改寫搜尋條件,來交叉評估不同的搜尋結果以取得期望的結果
相關性測試
相關性測試並非簡單工作,必須了解原理 & 多做分析 & 多做調整
可能會需要多 analyzer & boosting … 等參數做各式各樣的調整
每個環境跟需求對應到的設定 & 搜尋條件也都不會相同,不會有 silver bullet 般的設定可以一次解決所有問題
監控 & 理解用戶行為
使用 Search Template 和 Index Alias 查詢
主要的功能在於 de-couple 程式與查詢用的 DSL 兩者之間的關係,讓專業的工程師可以各司其職的完成工作(開發人員/查詢工程師/效能調校工程師)
程式設計師不需要了解查詢的優化細節,只要使用 ES 工程師提供的 Search Template 即可
ES 工程師則可以專注在效能的調校 & 優化 search template 工作上
以下是一個簡單範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 POST _scripts/tmdb { "script" : { "lang" : "mustache" , "source" : { "_source" : [ "title" , "overview" ] , "size" : 20 , "query" : { "multi_match" : { "query" : "{{q}}" , "fields" : [ "title" , "overview" ] } } } } } GET _scripts/tmdb POST tmdb/_search/template { "id" : "tmdb" , "params" : { "q" : "basketball with cartoon aliens" } } DELETE _scripts/tmdb
index alias 就跟 Linux 中的 alias 指令一樣,是作為設定別名的用途。
而通常為 index 設定別名是有其需要的,例如每天建立一個新的 index,但在程式中每天都根據日期去產生一個字串來作為 index 來查詢,其實挺麻煩的;此時透過設定一個名稱為 latest_index 並指到每天最新的 index 的方式,問題就迎刃而解了。
除了別名之外,甚至可以額外加入 filter 條件,先針對 index 資料內容進行 filter 後再查詢
以下是一個簡單範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 PUT /movies-2019 /_doc/1 { "name" : "the matrix" , "rating" : 5 } PUT /movies-2019 /_doc/2 { "name" : "Speed" , "rating" : 3 } POST _aliases { "actions" : [ { "add" : { "index" : "movies-2019" , "alias" : "movies-latest" } } ] } POST /movies-latest/_search { "query" : { "match_all" : { } } } POST _aliases { "actions" : [ { "add" : { "index" : "movies-2019" , "alias" : "movies-lastest-highrate" , "filter" : { "range" : { "rating" : { "gte" : 4 } } } } } ] } POST /movies-lastest-highrate/_search { "query" : { "match_all" : { } } }
綜合排序:Function Score Query 優化算分 Scoring & Sorting
可以在查詢結束後,對每一個符合的 document 進行重新算分,並根據新的分數來進行排序。
Elasticsearch 中已經包含了以下幾種用來算分的函數:(非全部,比較常用的,詳細資訊可參考官網 )
Weight:為每一個 document 設定一個簡單不被規範化的權重
Field Value Factor:可指定特定的 field 來影響算分過程,例如指定點讚數 作為算分的條件之一
Random Score:隨機算分
Decay Function:以某個 field 的值作為基準,距離越遠得分越高
Script Score:自己寫 script 來自定算分邏輯
以下用一個實際範例來說明使用方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 DELETE blogs PUT /blogs/_doc/1 { "title" : "About popularity" , "content" : "In this post we will talk about..." , "votes" : 0 } PUT /blogs/_doc/2 { "title" : "About popularity" , "content" : "In this post we will talk about..." , "votes" : 100 } PUT /blogs/_doc/3 { "title" : "About popularity" , "content" : "In this post we will talk about..." , "votes" : 1000000 } POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "function_score" : { "query" : { "multi_match" : { "query" : "popularity" , "fields" : [ "title" , "content" ] } } , "field_value_factor" : { "field" : "votes" } } } }
由於上面只根據 votes 欄位作為重新計算分數的依據,因此投票數超高的 document 得到了超高的分數。
但若是希望算分不要差距這麼大,希望做個平滑處理,那可以搭配 modifier & factor 兩個參數來完成,以下是示範範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "function_score" : { "query" : { "multi_match" : { "query" : "popularity" , "fields" : [ "title" , "content" ] } } , "field_value_factor" : { "field" : "votes" , "modifier" : "log1p" } } } } POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "function_score" : { "query" : { "multi_match" : { "query" : "popularity" , "fields" : [ "title" , "content" ] } } , "field_value_factor" : { "field" : "votes" , "modifier" : "log1p" , "factor" : 0.1 } } } }
Boost Mode & Max Boost 在 function score query 中同樣也可以加入 boost 的設定,並可以搭配多種不同的 boost mode 來調整計算分數時的基礎:
multiply: query score 與 function score 相乘(預設值)
replace: 忽略 query score,只使用 function score
sum: query score 與 function score 相加
avg: query score 與 function score 的平均值
max: query score 與 function score 兩者中較大的值
min: query score 與 function score 兩者中較小的值
以下是個簡單範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "function_score" : { "query" : { "multi_match" : { "query" : "popularity" , "fields" : [ "title" , "content" ] } } , "field_value_factor" : { "field" : "votes" , "modifier" : "log1p" , "factor" : 0.1 } , "boost_mode" : "sum" , "max_boost" : 3 } } }
一致性的隨機函數
以上的需求就可以透過 function score query 中的 Random Score 來達成:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 POST /blogs/_search { "query" : { "function_score" : { "random_score" : { "seed" : 911119 } } } }
其他參考資料
Term & Phrase Suggester Elastic 官網文件 - Suggester
什麼是搜尋建議?
搜尋建議的功能在 Elasticsearch 中是透過 Suggester API 來實現的
以 term suggester 為例,其運作原理在於將輸入的內容分解為 token,接著在索引的字典裡面尋找相似的 term 並回傳
目前 Elasticsearch 一共支援四種 suggester,分別是 TermPhraseCompletionContext
Term suggester 中還可以額外設定好幾個 suggestion mode,分別是:
以下是幾個簡單範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 DELETE articles POST articles/_bulk { "index" : { } } { "body" : "lucene is very cool" } { "index" : { } } { "body" : "Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene" } { "index" : { } } { "body" : "Elasticsearch rocks" } { "index" : { } } { "body" : "elastic is the company behind ELK stack" } { "index" : { } } { "body" : "Elk stack rocks" } { "index" : { } } { "body" : "elasticsearch is rock solid" } POST /articles/_search { "size" : 1 , "query" : { "match" : { "body" : "lucen rock" } } , "suggest" : { "term-suggestion" : { "text" : "lucen rock" , "term" : { "suggest_mode" : "missing" , "field" : "body" } } } } POST /articles/_search { "suggest" : { "term-suggestion" : { "text" : "lucen rock" , "term" : { "suggest_mode" : "popular" , "field" : "body" } } } }
每個回傳的 suggest 都包含了一個算分,這也代表著相似性(相似性越高,分數越高),相似性是由 Levenshtein Edit Distance 的計算方法來實作出來的,核心概念就是 一個詞變更了多少字元就可以和另外一個詞一致。
而相似性的設定部份也可以透過一些參數可以來控制,例如 max_edits
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 POST /articles/_search { "suggest" : { "term-suggestion" : { "text" : "lucen hocks" , "term" : { "suggest_mode" : "always" , "field" : "body" , "sort" : "frequency" } } } } POST /articles/_search { "suggest" : { "my-suggestion" : { "text" : "lucne and elasticsear rock hello world " , "phrase" : { "field" : "body" , "max_errors" : 2 , "confidence" : 0 , "direct_generator" : [ { "field" : "body" , "suggest_mode" : "always" } ] , "highlight" : { "pre_tag" : "<em>" , "post_tag" : "</em>" } } } } }
Fuzzy Query Fuzzy Query 也是以 Levenshtein Edit Distance 為基礎,使用 fuzzy 關鍵字,可以容忍使用者搜尋時輸入少量的錯誤,依然可以找到符合的結果,以下是簡單的範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 GET /movies/_search { "query" : { "fuzzy" : { "title" : { "value" : "intersteller" , "fuzziness" : 1 } } } } GET /movies/_search { "query" : { "fuzzy" : { "title" : { "value" : "inersteller" , "fuzziness" : 1 } } } } GET /movies/_search { "query" : { "fuzzy" : { "title" : { "value" : "inersteller" , "fuzziness" : 2 } } } }
Completion & Context Suggester 這個是搜尋體驗優化的另一個重要功能;這功能可以協助使用者在輸入每一個字元時,系統可以快速到後端查詢到與目前輸入字元相關的結果並給出查詢字串補全的功能。
此外,在 7.0 版後的 Elasticsearch,還提供了一個 [search_as_you_type](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/search-as-you-type.html) data type,用來協助使用者建置查詢字串自動補全的功能。
要使用 completion suggester,就必須要在 index mapping 的設定中進行相關設定:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 PUT articles { "mappings" : { "properties" : { "title_completion" : { "type" : "completion" } } } }
以下是實際的操作範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 POST articles/_bulk { "index" : { } } { "title_completion" : "lucene is very cool" } { "index" : { } } { "title_completion" : "Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene" } { "index" : { } } { "title_completion" : "Elasticsearch rocks" } { "index" : { } } { "title_completion" : "elastic is the company behind ELK stack" } { "index" : { } } { "title_completion" : "Elk stack rocks" } { "index" : { } } POST articles/_search?pretty { "size" : 0 , "suggest" : { "article-suggester" : { "prefix" : "e" , "completion" : { "field" : "title_completion" } } } }
如何實作 Context Suggester ?
以下是一個簡單的範例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 DELETE comments PUT comments PUT comments/_mapping { "properties" : { "comment_autocomplete" : { "type" : "completion" , "contexts" : [ { "type" : "category" , "name" : "comment_category" } ] } } } POST comments/_doc { "comment" : "I love the star war /movies" , "comment_autocomplete" : { "input" : [ "star wars" ] , "contexts" : { "comment_category" : "movies" } } } POST comments/_doc { "comment" : "Where can I find a Starbucks" , "comment_autocomplete" : { "input" : [ "starbucks" ] , "contexts" : { "comment_category" : "coffee" } } } POST comments/_search { "suggest" : { "MY_SUGGESTION" : { "prefix" : "sta" , "completion" : { "field" : "comment_autocomplete" , "contexts" : { "comment_category" : "coffee" } } } } }
關於 Precision(精準度) & Recall(招回率) 以 Precision(精準度) 來看: (盡可能返回較少的無關 document )
Completion > Phrase > Term
以 Recall(招回率) 來看: (盡量返回較多的相關 document )
Term > Phrase > Completion
以 performance 來看:
Completion > Phrase > Term
Cross Cluster Search
水平擴展的問題
若只有 single cluster,水平擴展是不能無限增加節點數的
當 cluster metadata(node, index, cluster status) 過大時,會導致更新壓力變大,單一個 active master 會成為效能的瓶頸,導致整個 cluster 無法正常工作
以前透過 tribe node 實現 cross node search,但因為問題不少,因此 Elasticsearch 5.3 已經沒有使用 tribe node,而是改用 Cross Cluster Search 功能來取代
Cross Cluster Search