基本概念:Index、Document 和 REST API
Index & Document 是比較偏向開發人員視角,是種邏輯概念
Node & Shard 是比較偏向維運人員的視角,是種物理概念
Document
Document 是可以被搜尋數據的最小單位(可能是 log 文件中的一筆紀錄 / 一部電影或唱片的相關訊息 / RDBMS 中的一筆 record)
Document 會被序列化成 JSON(由一堆 Key/Value 的資料組成,並有其資料格式) 格式,保存在 Elasticsearch 中
每個 Document 都有一個 UID(Unique ID),可自己指定或交由 Elasticsearch 自動產生
JSON document
包含多個 Key/Value 組合,就像是資料庫中的一筆資料
但跟資料庫不一樣的是,JSON 格式靈活不受限,不須預先定義格式
每個 Key/Value 的類型(string, number, boolean … etc) 可以自己指定或是由 Elasticsearch 幫忙推算
Metadata

document metadata 就是描述 document 本身屬性用的資料,通常會包含以下內容:
_index:document 所屬的 index 名稱_type:document 類型 (例如:_doc)_id:document ID_source:document 的原始 JSON 資料樣貌_version:版本訊息 (有這欄位就表示 ES 具有版本控管的能力)_score:查詢時的算分結果 (每次的搜尋都會根據 document 對於搜尋內容的相關度進行算分)
Index
index在 ES 中是個邏輯空間的概念,用來儲存 document 的容器,而這些 document 內容都是相似的 (跟其他領域的 index 用法不太一樣)shard在 ES 中則是個物理空間的的概念,index 中的資料會分散放在不同的 shard 中index 由以下幾個部份組成:
data:由 document + metadata 所組成mapping:用來定義每個欄位名稱 & 類型setting:定義資料是如何存放(例如:replication 數量, 使用的 shard 數量)
下圖是
setting的設定範例:
在 ES 7.0 的版本後,index 在
type部份只能設定為_doc(在以前的版本是可以設定不同的 type)
Elasticsearch 與 RDBMS 的比較 & 取捨
以下表格是 Elasticsearch & RDBMS 的對比:(不是完全符合,但概念上是很接近的)
| RDBMS | Elasticsearch |
|---|---|
| Table | Index |
| Row | Document |
| Column | Field |
| Schema | Mapping |
| SQL | DSL |
ES 是 schemaless 的,資料格式可以隨意定,非常適合用來做全文檢索 or 查詢與資料的相關性
RDBMS 的強項在於處理對於資料事務性(交易)要求特別高的任務
常用搜尋
在 Kibana Dev Tools 頁面中,可以直接下查詢語法,以下舉幾個與 index 相關的搜尋:
查詢 index
1 | # 取得指定 index 資訊,包含 mapping & setting ... 等資訊 |
搭配 _cat 做搜尋
1 | # 透過 _cat 查詢 index 相關資訊,搭配正規表示式 |

1 | # 加上過濾條件 |

1 | # 使用排序 |
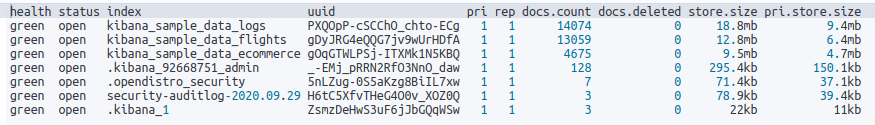
1 | # 查詢每個 index 所消耗的 memory 為多少,搭配排序 |
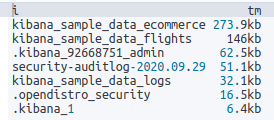
1 | # 加上過濾條件 |

1 | # 使用排序 |

1 | # 查詢每個 index 所消耗的 memory 為多少,搭配排序 |

Document 的基本 CRUD 與批次操作
Document CRUD
GET:取得 document- 語法為
GET _index/_type/[ID],例如 GET /users/_doc/1 - document 會有 version control 的功能,因此即使被刪除,version 欄位的值也會不斷增加
_source欄位包含了 document 的原始訊息
- 語法為

Create(PUT):- 建立新的 document,如果 ID 已經存在會發生錯誤
- 語法為
PUT _index/_create/[ID]orPUT _index/_doc/[ID]?op_type=create,例如:PUT /users/_create/1 (也可以不帶 ID,就會自動生成) - 較不建議指定 ID 的作法,可能會撞到效能不彰的問題
Create(POST)- 系統會自動產生 document ID (這是比較建議的方式)
- 語法為
POST _index/_doc
Index(PUT):- 如果 ID 不存在,則建立新的 document;若 ID 已經存在,則刪除現存的 document 再建立新的,version 的部份會增加
- 語法為
PUT _index/_doc/[ID],例如:PUT /users/_doc/1
Update(PUT):- PUT 其實也可以作為更新 document 用,但更新的範圍是整個 document
- 實際上,Elasticsearch document 是無法修改的;而更新這個操作其實是新增一個新的 document,將原有的 _version 加 1 後,舊的 document 被標示為 deletion
Partially Update(POST):- document 必須已經存在,更新時只會對 document 中相對應的欄位作增量更新 or 對應欄位的修改
- json payload 需要包含在
doc欄位中 (可參考官網文件) - 語法為
POST _index/_update/[ID],例如:POST /users/_update/1 - POST 也可以拿來作為新增 document 用
呼叫 API 時傳輸的數據不宜過大(預設單一個 document 大小不能超過 100MB),過大的 document 建議拆成 5~15MB 分次匯入
批次操作
批次操作基本上是用來提昇 API 呼叫時的效能
但每次的 API request 不要發送過多的資料,因為過多的資料可能會造成 ES cluster 過大的壓力導致效能下降(必須記得 ES cluster 每秒都需要服務相當多的 API request)
Elasticsearch 中支援幾種批次操作 API,常用的有以下幾個:
/_bulk
1 | POST /_bulk |
讓使用者可以在同一個 API request 中送出多個操作,支援 Index/Create/Update/Delete,提昇效率
request 中的每一筆資料都會有對應的 return code,其中的任何一個操作失敗不會影響其他操作
範例如下:
1 | POST _bulk |
/_mget
1 | GET /_mget |
- 一次讀取多個不同 index 中特定 ID 的 document
使用範例:
1 | GET /_mget |
[/_msearch]
1 | GET /<target>/_msearch |
一次作多個大範圍的搜尋
使用範例:
1 | GET my-index-000001/_msearch |
其他注意事項
大版本的升級,document 必須重建 index
Elasticsearch 預設會提供 dynamic mapping 的功能,因此不用預先設定好 index 結構;但在生產環境中,建議先做好 mapping 的設定後再寫入資料
透過 X-Pack security plugin,可以提供 index-level or field-level 的 role based 資料存取控制
API 行為區分
index: 針對整個文檔,既可以新增又可以更新;
create:只是新增操作,已有報錯,可以用 PUT 指定 ID,或 POST 不指定 ID;
update:指的是部分更新,官方只是說用POST,request body 裡用 script 或 doc 裡包含文檔要更新的部分;
delete 和 read:就是 delete 和 get 請求了,比較簡單
Inverted Index(倒排索引)介紹
Forward Index(正排索引):Document ID 到 Document 內容到單詞的關聯
Inverted Index(倒排索引):單詞到 Document ID 的關係
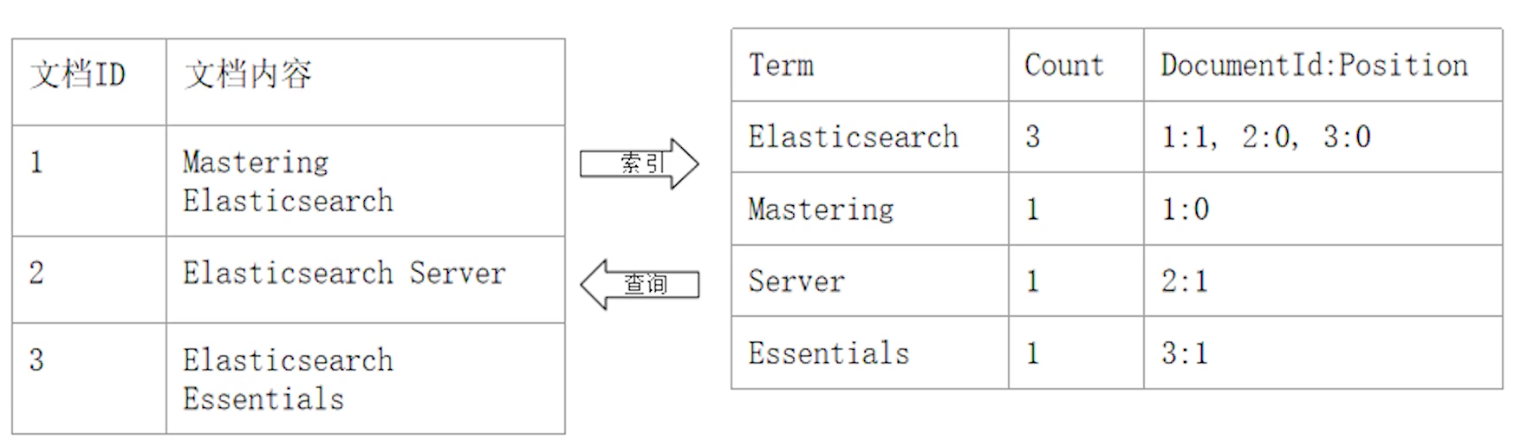
Inverted Index 組成
Term Dictionary (單詞辭典)
- 為了滿足快速的插入 & 查詢,且因為 term 的數量龐大,因此通過 B+ tree or Open Hashing 的方式實現
- 記錄 Document 中所有的單詞,記錄單詞到 posting list(倒排列表) 的關聯關係
Posting List (倒排列表):由 posting(倒排索引項組合) 組成,包含以下內容:
- Document ID
- 詞頻 (Term Frequency):term 在 document 中出現的次數,用在相關性評分
- 位置 (Position):term 在 document 的位置,用在搜尋
- 偏移 (Offset):記錄 trem 開始 & 結束位置,用於高亮顯示
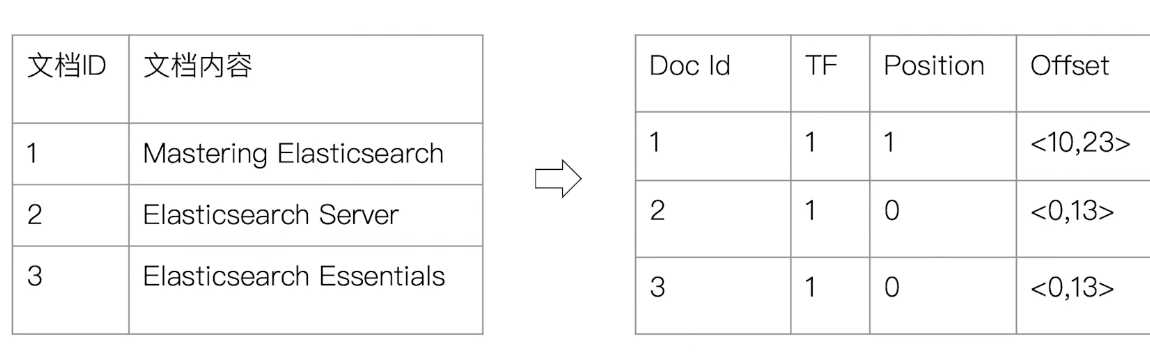
Elasticsearch 的 JSON document 中的 term 都會有自己的倒排索引
可以對某些欄位不作索引:
- 優點:節省儲存空間
- 缺點:該欄位無法被搜尋
References
通過 Analyzer 進行分詞
Analysis 是將 document 的內容轉換為一系列單詞(term/token) 的過程,也叫分詞
Analysis 是由 Analyzer 來實現,Analyzer 由
Character Filter->Tokenizer->Token Filter三個部份所組成,每個部份都可以自訂
Analyzer 的組成
Analyzer 是專門處理分詞的組件,由三個部份組成:
Character Filter:針對原始文件進行處理,例如:去除 HTML tagTokenizer:根據規則切分 termToken Filter:將分割後的 term 進行加工,例如:轉小寫、刪除 stopwords、增加同義詞、stemming(例如將 box, boxed, boxing … 等字轉換成 box)有時後會希望不要過濾 stopwords,而是直接把內容當成完整的 phrase 看待 (例如:to be or not to be)
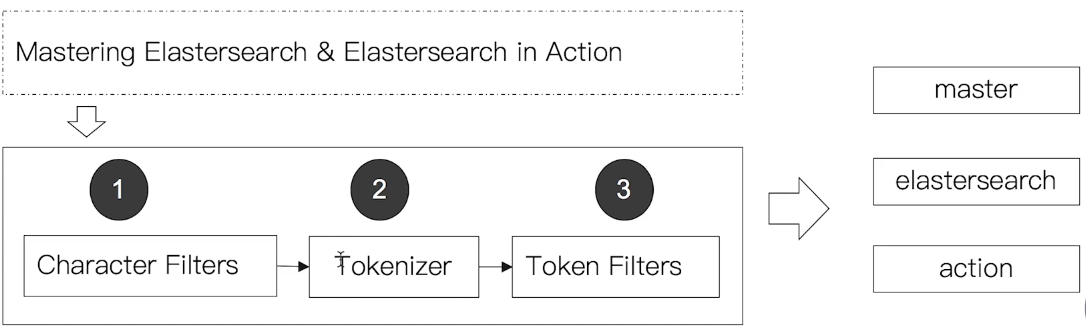
- Elasticsearch 內建很多 Analyzer,每個 Analyzer 會由不同的 character filter, tokenizer, token filter 組合而成,使用者也可以自訂 Analyzer
Elasticsearch 內建的 Analyzer
以下是幾個 Elasticsearch 內建的 Analyzer,有興趣的人可以試試看每個 Analyzer 處理完後資料的效果:
1 | # character filter: standard (按詞切分) |
Search API 概覽
- search API 分成
URI search(使用 GET) &request body search(同時支援 GET & POST,使用 ES 提供的 DSL)
查詢範圍:
| 語法 | 範圍 |
|---|---|
/_search |
cluster 上所有的 index |
/index1/_search |
index1 |
/index1,index2/_search |
index1 + index2 |
/index*/_search |
以 index 開頭的 index |
搜尋與相關性
搜尋行為是客戶對於搜尋引擎的操作 & 互動
客戶關心的是搜尋結果的相關性:
- 是否可以找到相關的內容?
- 搜尋結果中包含了多少不相關的內容?
- 搜尋結果的算分是否合力
- 結合實際業務需求,平衡搜尋結果的排名
衡量相關性
Information Retrieval
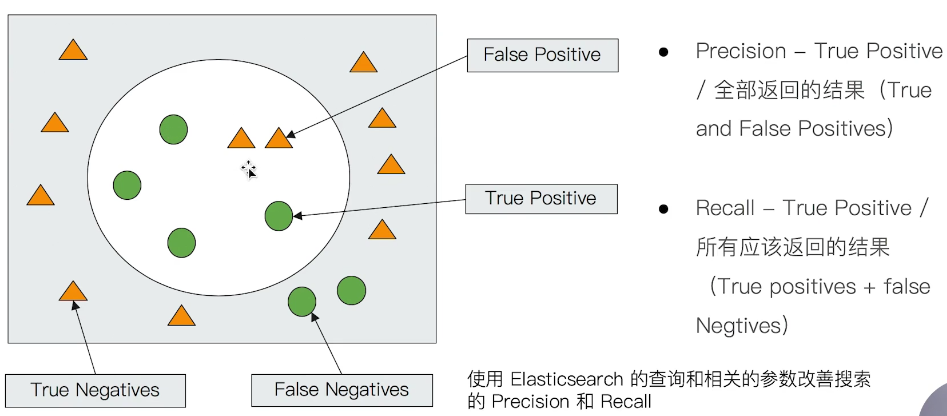
Precision (查準率):盡可能返回較少的無關 document
Recall (查全率):盡量返回較多的相關 document
Ranking:是否能夠依照相關度進行排序?
URI Search詳解
URI search 範例:
1 | GET /movies/_search?q=2012&df=title&sort=year:desc&from=0&size=10&timeout=1s |
q:指定查詢語句,使用 Query String Syntaxdf:預設查詢的 field,若不指定則會對所有的 field 進行查詢sort:排序from&size用於分頁profile:可以檢查查詢是如何被執行的
搜尋範例
1 | # 基本查詢 |
GET /movies/_search?q=2012&df=title==GET /movies/_search?q=title:2012
1 | # 泛查詢 => 對所有的 term 進行查詢 |

1 | # 在 title 中尋找 "Beautiful OR Mind" |

1 | # 使用引號 => "Beautiful Mind" = "Beautiful AND Mind" |


1 | # 使用括號 => (Beautiful Mind) = "Beautiful OR Mind" |

1 | #正規表示式查詢 |
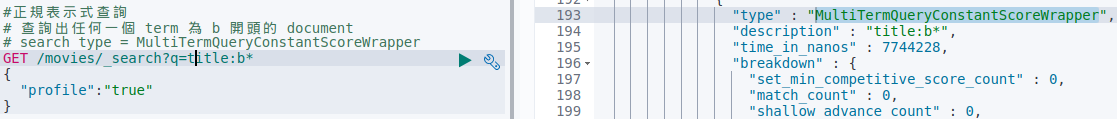
查詢效率低,記憶體消耗大,不建議使用
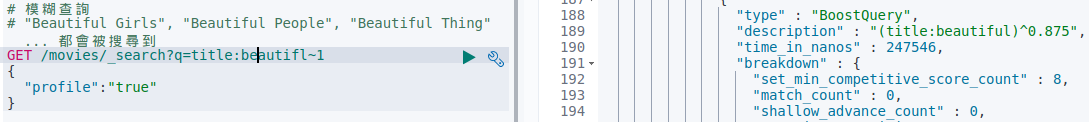
1 | # 模糊查詢 (即使 search term 有輸入錯誤,還是可以查詢) |

Request Body 與 Query DSL 簡介
- 進階的查詢通常只能用 request body 的方式完成
一般查詢範例
1 | # ignore_unavailable=true,可以忽略嘗試訪問不存在的 index “404_idx” 導致的錯誤 |
Scripted Field(腳本欄位) Query
1 | # 透過 ES 中 painless script 算出新的 field value |
使用查詢表達式 - Match
1 | # 預設為 "last OR christmas" |
使用查詢表達式 - Match Phrase
1 | # 必須按照順序出現 |
Query String & Simple Query String 查詢
Query String Query
- 類似 URI Query
1 | # 可指定 default field(DF) |
Simple Query String Query
類似 Query String, 但會忽略錯誤的語法,並且僅支援部份查詢語法
不支援 AND/OR/NOT,會當作 term 來處理
term 之間預設的關係是
OR,可指定operator支援使用
+取代AND,|取代OR,-取代NOT
1 | POST /users/_search |
Dynamic Mapping 和常見欄位類型
What is Mapping ?
Mapping 類似資料庫中的 schema 定義,用途如下:
定義 index 中每個 term 的名稱
定義每個 term 的資料型態,例如:string, Interger, boolean
term & inverted index 的相關配置 (要使用哪個 Analyzer,或是不被索引)
Mapping 會將 JSON document 映射成 Lucene 所需要的扁平格式
一個 Mapping 屬於一個 index type
每個 document 都屬於一個 type
一個 type 都會有一個 mapping 定義
7.0 開始,不需要在 mapping 定義中指定 type 資訊
Term Data Type
簡單類型
Text / Keyword
Date
Integer / Floating
Boolean
IPv4 & IPv6
複雜類型
Object
List
特殊類型
geo_point & geo_shape (地理訊息)
percolator
What is Dynamic Mapping ?
在寫入 Document 時,如果 index 不存在,則會自動建立 index
Dynamic Mapping 可以根據 Document 內容,推算出 term data type 並自動建立 mapping,因此不需要手動制定
但推算的結果不一定會完全正確(例如:地理位置相關訊息可能會推斷錯誤)
term data type 推算錯誤可能會導致某些查詢無法正常使用,例如:range 查詢
若是濫用 Dynamic Mapping,導致不斷有新欄位出現卻不管制,cluster state 會一直變更調整,而這樣的調整會需要同步到 cluster 中的所有 node 上,若是因為大量的 field mapping 而導致更新 cluster state 的操作若是太頻繁,很有可能會導致記憶體不足的問題發生,甚至會導致 cluster 掛掉,這現象稱為
Mapping Explosion
範例
簡單測試 Dynamic Mapping:
1 | # 寫入 document,mapping 會動態產生 |
故意將某些資料類型加上雙引號測試:
1 |
|
修改 Mapping 中的欄位類型
在新增加欄位的情況下:
若 dynamic = true,一旦有新增欄位的 document 寫入時,mapping 資訊也會同時被更新
若 dynamic = false,mapping 不會被更新,新增欄位的資料無法被索引,但是資料會出現在
_source中若 dynamic = strict,寫入 document 的操作會發生錯誤
若是針對已經存在的欄位,使用其他欄位類型的資料進行寫入操作,是無法變更 mapping 設定的,因為一旦當 reverted index 已經生成後,就無法修改;而若是真的要改變欄位類型,則是需要透過 Reindex API 來重建索引。
若是原有欄位的數據類型可以隨意修改,這樣會讓原本已經被索引的資料無法被搜尋
| Dynamic Mapping 設定 | “true” | “false” | “strict” |
|---|---|---|---|
| document 可索引 | Yes | Yes | No (資料寫入會錯誤)) |
| 欄位可索引 | Yes | No | No |
| Mapping 被更新 | Yes | No (新增欄位被丟棄) | No |
修改 Mapping 範例
1 | # 預設 dynamic mapping 開啟,寫入新的 document 進 index 中 |
顯式 Mapping 設置與常見參數介紹
自定義 mapping
往 index 送 PUT request 並帶上 mappings 設定即可:
1 | PUT movies |
撰寫 mapping 其實不是這麼容易,除了可以參考 API 來撰寫之外,也可以透過寫入一些 sample data 到一個臨時的 index,讓 Elasticsearch 自動產生 mapping 定義後,再根據實際需求進行修改。
Index Options
Inverted Index 根據要記錄的內容,有四種 index options 可以設定:
| Index Option | Inverted Index 中的記錄內容 |
|---|---|
docs |
doc id |
freqs |
doc id + term frequency |
positions |
doc id + term frequency + term position |
offsets |
doc id + term frequency + term position + character offsets |
type
text預設使用positions,其他則為docs記錄的資料越多,需要儲存空間越多
選擇性的讓特定 Field 不被索引
預設情況下每個 field 都會被索引,但若是確定特定的 field 資料不需要被查詢,也可以不被索引:
1 | PUT /users |
NULL value 的處理
1 | PUT /users |
copy_to 設定
透過 copy_to 的設定可以新增一個 field,實現類似 _all 的效果:
1 | PUT /users |
_all在 ES 7 後被copy_to取代上述範例中,使用者可以針對
fullName進行搜尋fullName的資料不會出現在_source中
Aray Type
目前 Elasticsearch 不支援 array type,但每個 field 都可以包含多個相同類型的數值:
1 | //新增一個帶有 string array 的資料 |
表示
texttype 其實是可以記錄 array type 的資料 (其實其他 type 也是可以記錄 array type 資料,例如:long))
Multiple Field 特性及 Mapping 中配置自定義 Analyzer
multiple field 資料中,可透過
keywordfield 作精確搜尋若是要做全文搜尋,則是使用
textfield 並搭配不同的 analyzer & search analyzer
1 | PUT products |
Exact Values v.s. Full Text
Exact Value 包含數字/日期/或是特定的字串(例如:”Apple Store”),在 Elasticsearch 中的
keywordfield 存放的就是這一類的資料Full Text 則是非結構化的資料,在 Elasticsearch 中的
textfield 存放的就是這一類的資料Exact Values 不需要做分詞處理,而 Full Text 則會需要分詞處理才能更容易被後續利用
自訂分詞器(Analyzer)
Analyzer 是專門處理分詞的組件,由三個部份組成:
Character Filter (針對原始文件進行處理,例如:去除 HTML tag)
Tokenizer (根據規則將資料切分 term or token)
Token Filter (將分割後的 term 進行加工,例如:轉小寫、刪除 stopwords、增加同義詞)
Character Filter
可同時設定多個 Character Filter
會影響 Tokenizer 的 position & offset 的資訊
目前 Elasticsearch 內建提供的 Character Filter 有 HTML strip、Mapping、Patter replace …等等
Tokenizer
只能設定一個 tokenizer
將 Character Filter 處理過後的資料,按照一定的規則,切分為詞(term or token)
目前 Elasticsearch 內建提供的 tokenizer 有
whitespace/standard/uax_url_email/pattern/keyword(不做任何處理)/path hierarchy也可以用 Java 實作自己的 tokenizer
Token Filter
可同時設定多個 Token Filter
將 Tokenizer 輸出的 term(or token) 進行增加、修改、刪除
目前 Elasticsearch 內建提供的 Token Filter 有
lowercase/stop/synonym… 等等
範例
1 | POST _analyze |
1 | POST _analyze |
1 | POST _analyze |
1 | //char filter 替換表情符號 |
1 | GET _analyze |
1 | GET _analyze |
也可以完全自己定義一個 Analyzer:
1 | PUT my_index |
Index Template 和 Dynamic Template
- 若 cluster 是用來做 log 管理,每天都產生一個專屬的 index 存放 log,數據管理上較為合理,效能表現也會較好
Index Template
Index Template 使用來協助使用者設定 mappings & settings 的相關規則,並可透過套用 template 建立新的 index 來取得在 template 中已經存在的設定
index template 只有在建立 index 有用,後續修改 template 不會影響已經存在的 index
可以設定多個 index template,這些設定會被合併在一起
也可以透過指定
order,來調整 index template 合併的過程
那 index template 是如何在 index 被新增時運作的呢?
先選用 Elasticsearch 中預設的 settings & mappings
先套用 order 值低的 index template 中的設定
再套用 order 值高的 index template 中的設定,並覆蓋之前的設定
如果建立 index 時使用者有指定 settings & mappings,就會覆蓋 index template 的設定
以下透過簡單範例,說明 index template 的建立跟使用時實際的流程:
1 | //建立 default index template |
Dynamic Template
dynamic template 相較於前面提到的 index template,擁有比較彈性的方式來制定 template,例如:
將所有 field 都設定成 keyword,或是關閉 keyword field
將
is開頭的 field 都設定為 boolean將
long開頭的 field 都設定為 long 類型
1 | //使用內建的自動辨識 |
1 | //移除原本的 index |
一個以 path 為基礎,並搭配較為複雜處理的設定:
1 | //移除原本的 index |
Elasticsearch 聚合分析簡介
Aggregation
Elasticsearc 除了一般的搜尋之外,也可透過 aggergation 的方式,提供數據統計分析的功能,可作到很即時的查詢
透過 aggregation 可以得到分析 & 總結數據後的總覽,而非單一 document,例如:
某特定區域剩餘的客房數量
進行不同價格區間的搜尋,可預定的平價旅館 & 五星級酒店的數量
效能很好,在 ES 端就可以得到分析結果,不用在 client 端開發分析邏輯
許多 Kibana 報表中的元素都可以透過 aggregation 的數據來完成。例如:
公司員工的職位分佈、薪水分佈
客戶所在的地理位置分佈
訂單的增減狀況
Aggregation Family (聚合總類)
Bucket Aggregation:滿足特定條件的 document 集合 (類似傳統 SQL 語法中的
Group By)Metric Aggregation:可透過數學運算,對 document filed 進行統計分析
基於數據集合計算結果;除了支援在 field 上進行計算,也支援在 (painless) script 產生的結果之上進行計算
大多數的 metric 是數學計算,只會輸出一個值,例如:min / max / sum / avg / cardinality
部份的 metric 支援輸出多個值,例如:stats / percentiles / percentile_ranks
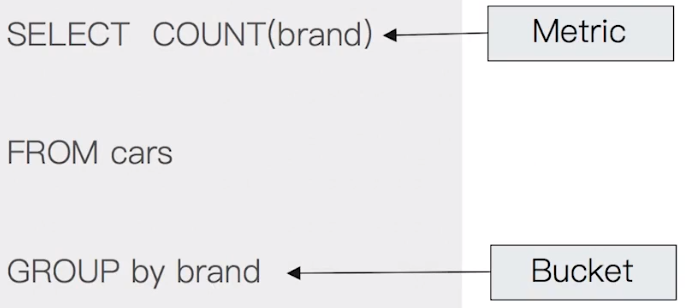
Matrix Aggregation:支援對多個 field 同時進行操作並提供一個結果矩陣
Pipiline Aggregation: 對其他 aggregation 的結果再一次的進行 aggregation
Histogram Aggregation:可以針對特定欄位值,指定範圍後一次產生多個 bucket 並統計各範圍的區間值,而統計區間一般是使用數值值型的欄位,但也可以使用日期欄位
範例:Bucketing (分桶)
1 | //根據目的地進行 bucketing 操作 |
範例:Bucketing + Metric
這是 aggregate 後再 aggregate 的範例:
1 | //查看航班目的地的統計資訊,並以目的地為單位,額外增加平均,最高最低價格 |
範例:Bucketing + Metric + Matrix
1 | //查看航班目的地的統計資訊,並以目的地為單位,額外增加平均票價 & 目的地天氣的統計資訊 |
範例:Histogram
1 | //查看 price 欄位以 50 為區間的 histogram 資訊 |